
SWOT analysis is a robust strategic management method. It focuses on the evaluation of the internal and the external environment of the enterprise. Through the analysis of the core four factors, companies acquire insights to enable them to manage resources correctly and set achievable objectives. (SWOT Full Form: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats)
It assists organizations in detecting strengths, weaknesses and securing opportunities for gaining competitive edge thus, proving useful for strategic development. Useful in all types of business – startup or enterprise, SWOT analysis helps match tactics to the environment, and as a result, helps preserve a competitive advantage in the respective field of business. In this article, we will explore everything you want to know about SWOT Analysis with SWOT Analysis examples, SWOT Analysis Template etc.
SWOT analysis is crucial in tactical plans since it helps the organization detect critical success factors in the most efficient way possible. Due to the revelation of strong points, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, it offers a clear picture that leads to the right decisions. In risk management, SWOT is useful to identify the challenge that may be in the way and then plan on how the challenge may be avoided.
It also saves time and resources by focusing on using time, money, and other resources on a company’s areas of strength. Moreover, opportunity finding is made possible by SWOT analysis since it shows trends within the market or industries which can be exploited.
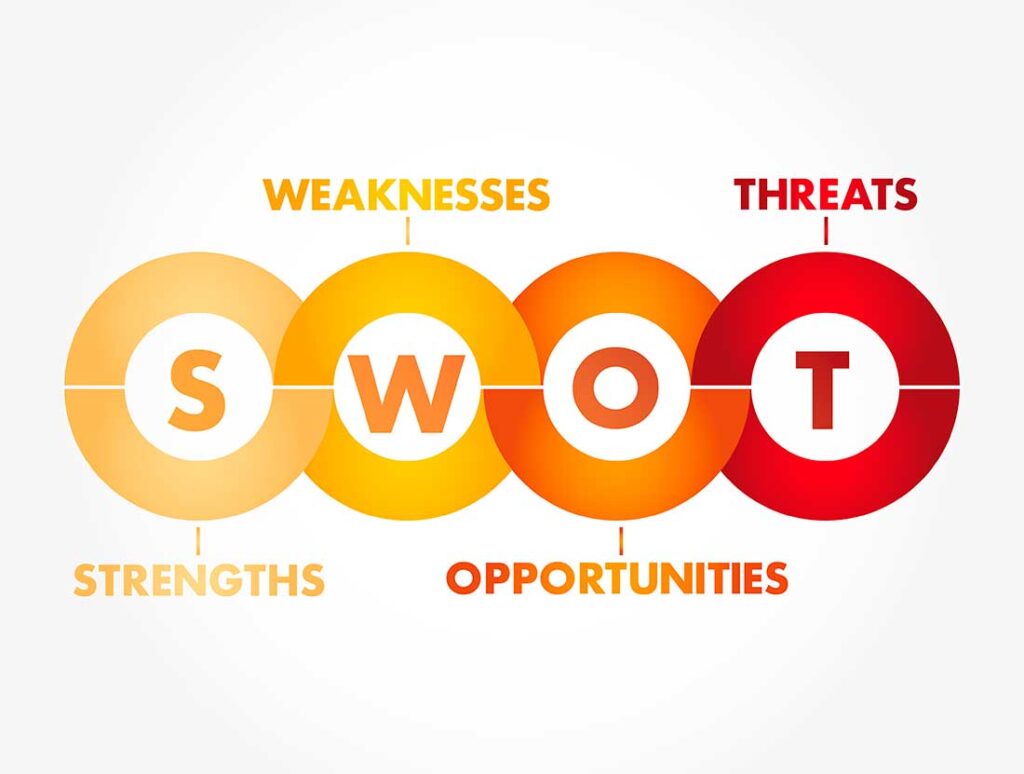
SWOT analysis is composed of four crucial components – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats which help in analyzing a business and its strategic trajectory. Opportunities are unrivaled advantages recognized and available inside the business, including brand image, skilled professionals, or advanced technology. These are recognized to help leverage on what the business does best. Weaknesses are internal unfavorable factors like absence or deficiency of an organization’s resources, inadequate or deficient technical proficiency or organizational performance that restricts growth.
Opportunities on the other hand are outside conditions that can also be capitalized on and they include market opportunities that include trends, technologies or population trends. These help businesses find ways of entering a market or developing the product line in some other capacity.
Threats are associated with unfavorable conditions that may be beyond a company, for instance, the emergence of other competitors, change in laws and regulations or change in economic factors. Based on the threats, it is possible to develop preventive measures that will help to protect business from possible turbulence. Such components enable organizations to maintain flexibility, downstream focus, and readiness for future development at the strategic level. Let’s deep dive into every aspect of SWOT analysis.
In the ‘Strengths’ or capability quadrant, organizations identify their internal strengths relative to the competition. These are aspects that the business has some degree of influence on, and can thus harness to give it competitive advantage.
Some examples of such attributes are; Well-established brand image, experienced and committed employee, unique and proprietary technology, and customer base. Locating and maximizing these strengths contributes to the organization gaining increased robustness, refining its performance and generating greater market growth. When businesses know their core strengths, it becomes easier to scale and grow.
In a SWOT analysis, “Weaknesses” refers to internal factors that may swamp an organization’s ability and capacity to prosper, turn a profit or compete effectively. It is encourageable factor that needs more attention to enhance general performance. Such include; inadequate capital, use of outdated equipment, limited market coverage, or inadequate quality products.
It helps a business to know which areas need improvement, cut on costs, eliminate unnecessary procedures, and focus resources well to improve on. Addressing the above areas systematically avoids potential obstacles, and lays down the foundation for continued growth in an organization and its competitive success.
In the context of SWOT analysis, “Opportunities” are the external conditions that may, if leveraged, help achieve benefits which could lead to the development of competitive strength. These favorable conditions outside the organization offer an opportunity to improve performance and market share.
Some strategies include new expansion into cognate markets, embracing technological innovations as well as embracing new trends in the industry. Therefore, while identifying these opportunities, firms are in a position to mobilize resources, build strategic initiatives and preemptively react to the forces of competition. It will assist them to build a strong position and overcome their rivals in the markets.
The last is the “Threats” which refers to factors that are unfavorable towards the existence and progress of the organization. These challenges are capable of detracting from performance and should therefore be managed with skillful anticipation of their effects.
Some examples are new entrants, the threat of globalization, the threat of increased sensitivity among consumers to certain issues, and the political threat that may influence the operation of a firm.
Knowing these threats will help the business to create countermeasures to defend its interest, increase its capacity to respond to change, and position itself for market success.

In SWOT analysis, internal factors are factors within the company’s control; these include; resources, strength of the team and the efficiency of operations. All these factors can be further fine-tuned to improve performance – and therefore create growth.
On the other hand, external factors are conditions in the environment and beyond the organization’s control such as competition, new regulation, and changing customer preferences.
The relation between internal and external factors is significant here. They can be used to exploit opportunities in the business environment or to neutralize threats and, conversely, could hamper the organization’s ability to effectively manage threats in the environment.
Moreover, unlike SWOT, PEST analysis also automatically covers external factors that impact the organization. Among these there are political, economic, social, and technological factors of the strategic context of the organization.
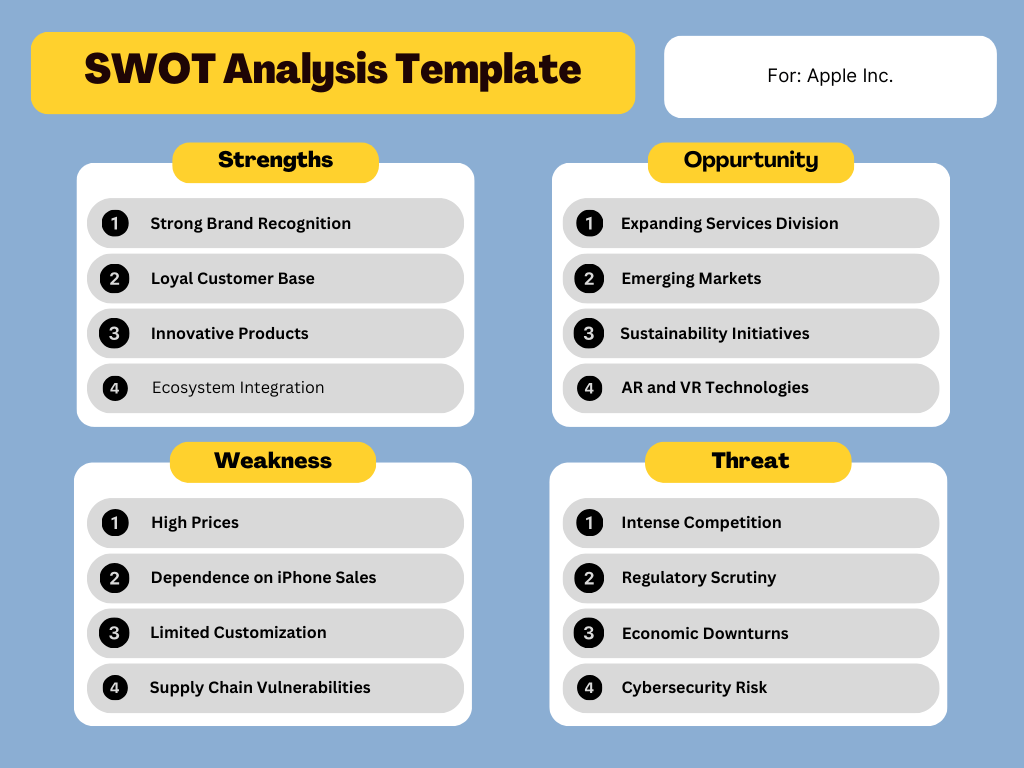
(Apple SWOT Analysis)
It is crucial for organizations interested in improving a competitive advantage and planning the sustainable development to learn how to implement a SWOT analysis. On this basis, several advantages can be distinguished and we can list, amongst the others, the following:
By using strengths businesses can capitalize on the key attributes, which can underline the competitive position of an enterprise. Reducing threats means dealing with internal vulnerabilities that may negatively impact performance and thus creating a more sound operational environment. It can be described as the process of actively capturing those trends and needs for growth which are favorable to the organization.
Besides, threat moderation is used to recognize certain dangers and take actions to protect an organization from possible external impacts. All the mentioned strategies lay down a structure that ensures appropriate choices for the future and the growth of a company. On this note, let’s explore every strategy in detail:
Ultimately, strengths must be mobilized to serve market opportunities or specific areas of competitive advantage. This may mean saying something that is new and different, better service, or being recognized for having a great brand. Realizing these internal factors, businesses could build on a competitive edge, attract new clientele and encourage the existing consumers’ loyalty hence guaranteeing growth and prosperity in an ever-evolving market landscape.
Managing weaknesses involves moving proactively to recognize and alleviate internal threats. These problems lead to the fact that organizations should do a deep analysis of the problem, find out what needs to be improved, for example, technologies or staff skills. Obviously, practice includes such activities as managing specific training initiatives, improving systems, or redistributing resources to improve organizational effectiveness. If these weaknesses are approached in a methodical way, companies are in a much stronger position in the long run to expand or grow even more than they currently are.
Opportunity capturing entails developing a good understanding of customers’ requirements within the specific market. Market research studies should be conducted within organizations in order to establish areas of growth within the organization; will entail diversification of products or venturing into other markets. Awareness of such conditions enables business to proactively respond through a combination of marketing measures, strategies, or partnerships that will enable businesses to take on favorable positions that are hard for competitors to emulate within the industry.
It is also important to develop a scope for risk management strategies and measures foreseen to prevent possible threats damaging business continuity. Organizations should analyze key risks that might threaten the management of resources, for instance, economic risks and competition risks. Examining possible prevention measures – establishing new revenues, improving the customer experience, or outlining the measures for dealing with a crisis – will limit the negative effects of those risks.
In conclusion, it is crucial to conduct a SWOT analysis for any business organization regardless of its size because it encompasses the inside and outside picture of strengths and weaknesses, and opportunities and threats. This powerful approach is not only helpful in avoiding worst-case scenarios, and analyzing various scenarios, but will also help organizations to manage their goals and resources effectively.
Using the results of a SWOT analysis, businesses can build the competitive advantage and apply the necessary changes more easily. Thus, readers are encouraged to apply the discussed strategies and use SWOT analyses with updates as frequently as needed.
Your knowledge can play a huge role in determining the success of your organization and thus do not hesitate to share your own SWOT stories. Also, you are welcome to use the provided SWOT template for your instance and get a start in your analysis. Be introduced to the first step of effective strategic planning!